Melanoma
Understanding Melanoma: Risks, Detection, and Prevention
Melanoma is a dangerous type of skin cancer that occurs in melanocytes, which are the cells that produce the skin pigment known as melanin. Though melanocytes are usually found in the skin, they are also present in the bowel, the eyes, and other areas of the body; however, the risk of melanoma in these areas is very low compared to that of the skin.
While melanoma is less common than other forms of skin cancer, it is the deadliest and is responsible for approximately 75% of all skin cancer deaths. Around 160,000 new melanoma cases are diagnosed in the U.S. each year. Excessive ultraviolet light (UV) exposure contributes significantly to one’s risk of developing melanoma.
Regular skin checks by a dermatologist are crucial in detecting melanoma, a potentially life-threatening form of skin cancer. Dermatologists possess the expertise to identify suspicious moles, lesions, or changes in the skin that might indicate melanoma. Equally important are self-exams, where individuals monitor their skin for any alterations in moles' shape, size, color, or the appearance of new spots.
By combining professional evaluations with self-examinations, early detection becomes more likely. Timely intervention significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and better outcomes for melanoma, underscoring the importance of regular checks by both dermatologists and self-exams for everyone's overall skin health.
Your skin health is our top commitment at The Skin Surgery Center. Our expert providers are ready to take care of you and your loved ones throughout their entire skin wellness journey. We offer comprehensive care and advanced treatments to ensure the best outcomes for all our patients. Protect your skin by scheduling regular check-ups and being vigilant about any changes. Your proactive approach can make a significant difference in maintaining healthy skin.
Examples of Melanoma
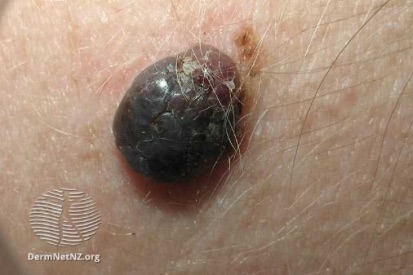
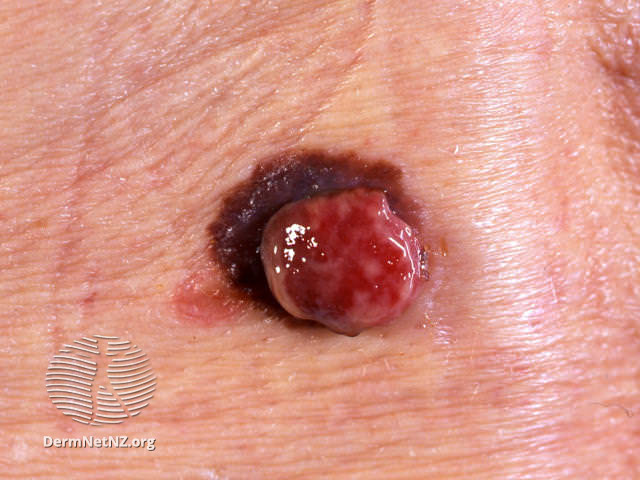
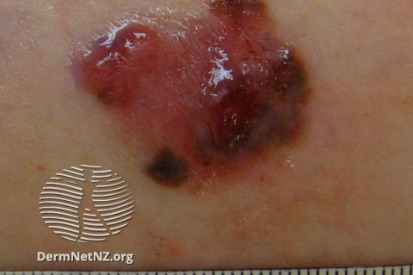
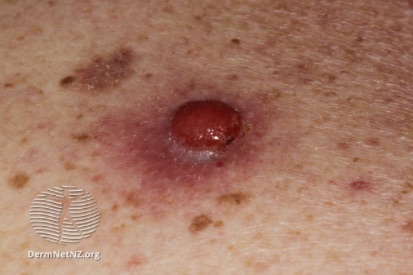
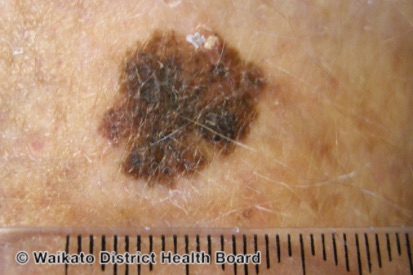
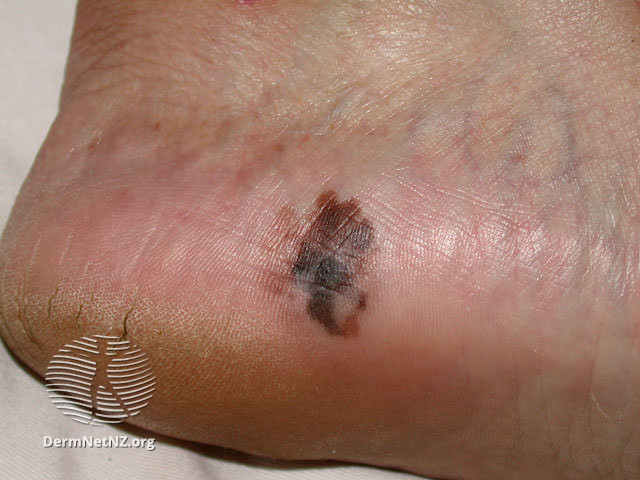
Symptoms of Melanoma
- Melanoma most often presents itself with the change of an existing mole, including change of symmetry, color, or shape.
- Irregular mole borders – scalloped, wavy, or notched.
- Diameter - anything new growing in size.
- Moles that itch, ooze or bleed.
- Melanoma can appear on normal skin tissue and does not always start as a mole.
What Causes Melanoma?
- Melanoma is primarily caused by the uncontrolled growth of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) in the skin.
- Melanoma is often triggered by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or tanning beds.
- Genetic factors and a history of severe sunburns also contribute to the development of melanoma.
How to Prevent Melanoma
Melanoma Frequently Asked Questions
The main cause of melanoma is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, either from sunlight or tanning beds. Other risk factors include having fair skin, a history of sunburns, numerous moles, a family history of melanoma, and a weakened immune system. If these risk factors apply to you, it's important to schedule regular Total Body Skin Exams.
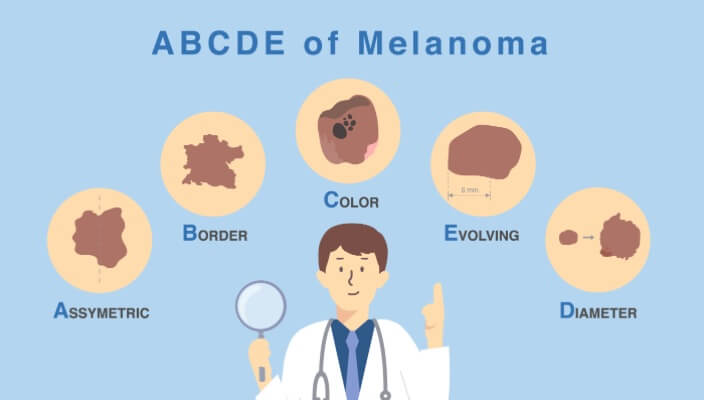
Diagnosis involves a biopsy, where a sample of the suspicious area is removed and examined under a microscope. Dermatologists may use the ABCDE rule (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variations, Diameter larger than 6mm, Evolution or change) to assess whether a mole may be melanoma.
Melanoma is staged from 0 to IV, with stage 0 being melanoma in situ (confined to the top layer of skin) and stage IV indicating the cancer has spread to other organs. Staging helps determine the extent of the disease and guides treatment decisions.
Treatment options for melanoma depend on the stage of the cancer and may include surgical excision, lymph node removal, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy. The choice of treatment is individualized based on factors such as the patient's overall health and the characteristics of the melanoma.
From Our QualDerm Family of Providers: Melanoma Treatment Options
Melanoma Treatment Options
We will confirm melanoma through a biopsy and pathological examination and then treat appropriately.
Treatment options for melanoma provided by a dermatologist may include surgical procedures to remove the cancerous tissue, such as excision or Mohs surgery. Additionally, your dermatologist may recommend therapies like immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the stage and characteristics of the melanoma. Close monitoring, regular skin checks, and collaboration with other specialists ensure effective treatment and reduce the risk of recurrence.
If you notice unusual growths on your skin as mentioned above, we highly recommend scheduling an appointment with one of our providers. Annual skin checks are essential for early detection.
Early detection and treatment are crucial elements of comprehensive skin cancer care.
Featured Blogs
- Skin Cancer
- Skin Exams
Discover the ABCDEs of melanoma. Familiarize yourself with the five key indicators to aid in early detection and prompt medical attention for any suspicious moles or skin lesions.
Read More
- Skin Cancer
- Skin Exams
It’s time to face the facts: skin cancer can develop in individuals of all skin colors, including those with darker skin tones.
Read More
- Skin Cancer
- Skin Exams
In this blog, we’re covering what you need to know about five dangerous skin cancers, including basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), malignant melanoma, merkel cell carcinoma, and kaposi sarcoma.
Read MoreFeatured Products for Sun Protection

EltaMD UV Replenish SPF 44
UV Replenish Broad-Spectrum SPF 44 is a 100% physical actives sunscreen that restores moisture to dry, stressed skin. Formulated with chemical-free active ingredients, it provides gentle yet effective sun protection. UV Replenish infuses the skin with hyaluronic acid that helps retain more than 1,000 times its weight in water within skin cells. Antioxidant activity further works to combat skin-aging free radicals associated with ultraviolet (UV) and infrared radiation (IR). It offers high-energy visible (HEV) light protection. This oil-free sunscreen feels weightless on the skin. Ideal for daily and active wear, it may be used by all skin types and after treatments as directed by a skin care professional. 2 oz

EltaMD UV Sport SPF 50 3oz, 7 oz
Have your fun in the sun – but play it safe. This sunscreen is great for swimmers, skiers, runners, golfers and other athletes – or for those who just love to be outdoors! UV Sport is water-resistant, so it won’t rinse off in water or drip into your eyes and sting when you sweat.


